What is MVC?
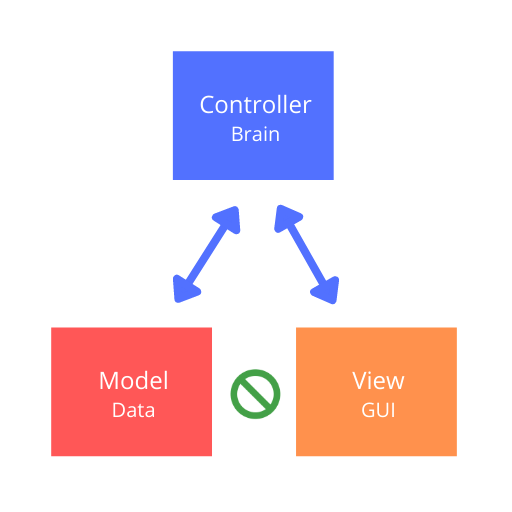
MVC stands for Model-View-Controller. MVC is an application design model consisting of three interconnected parts. They include the model (data), the view (user interface), and the controller (processes that handle input).
MVC is a well-known model for designing web applications. Programming languages like JavaScript, Python, Ruby, PHP, Java, C#, and Swift have MVC frameworks that are used for web or mobile application development.
How does MVC work?
The Model is responsible for managing the data of the application. It receives user input from the Controller.
The View is responsible for the presentation of the Model (data) in a certain format.
The Controller receives the user input and validates it, and then passes the input to the Model. It performs interaction on the model objects.
Advantages of MVC Framework
- Parallel development
- Code reusability
- Multiple views for a model
















